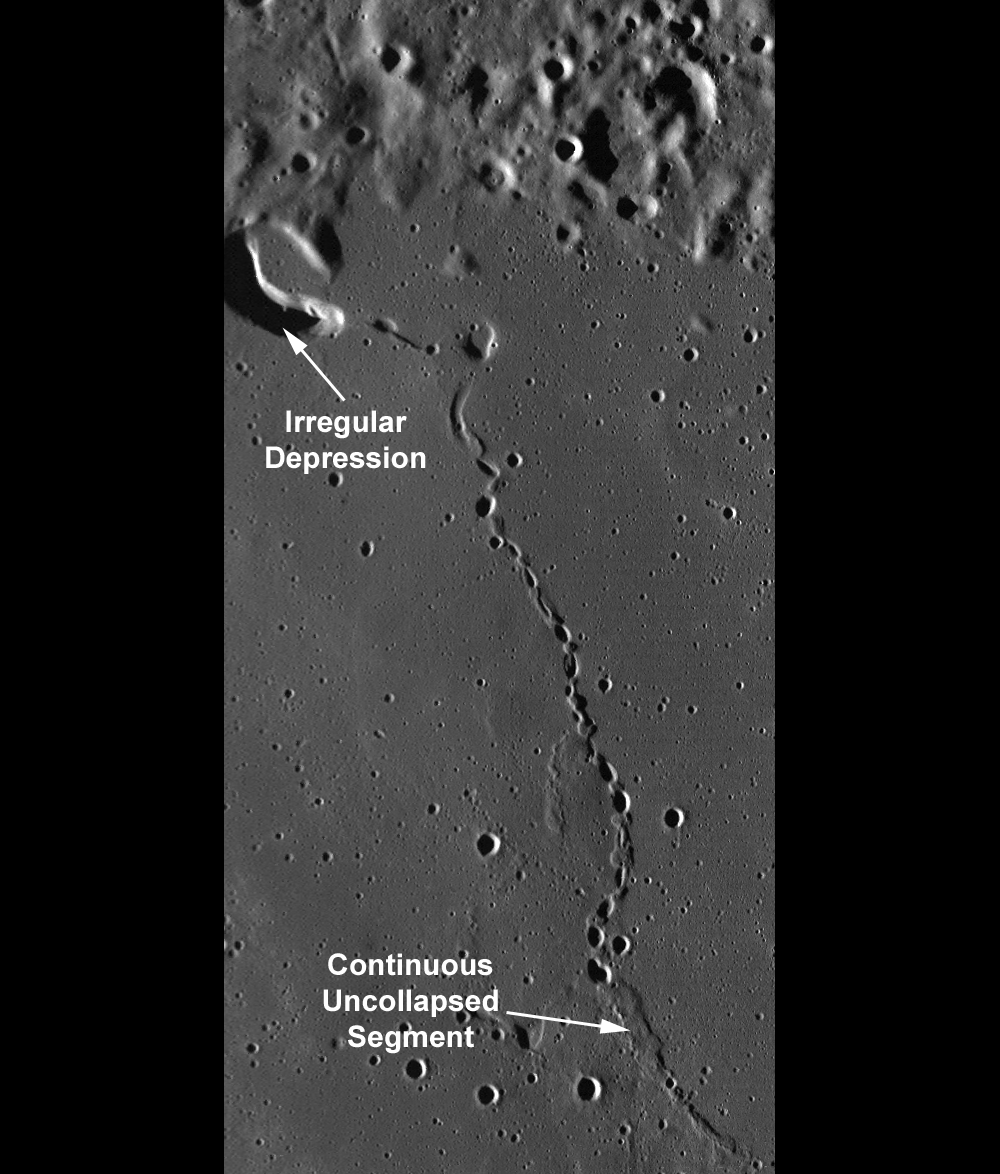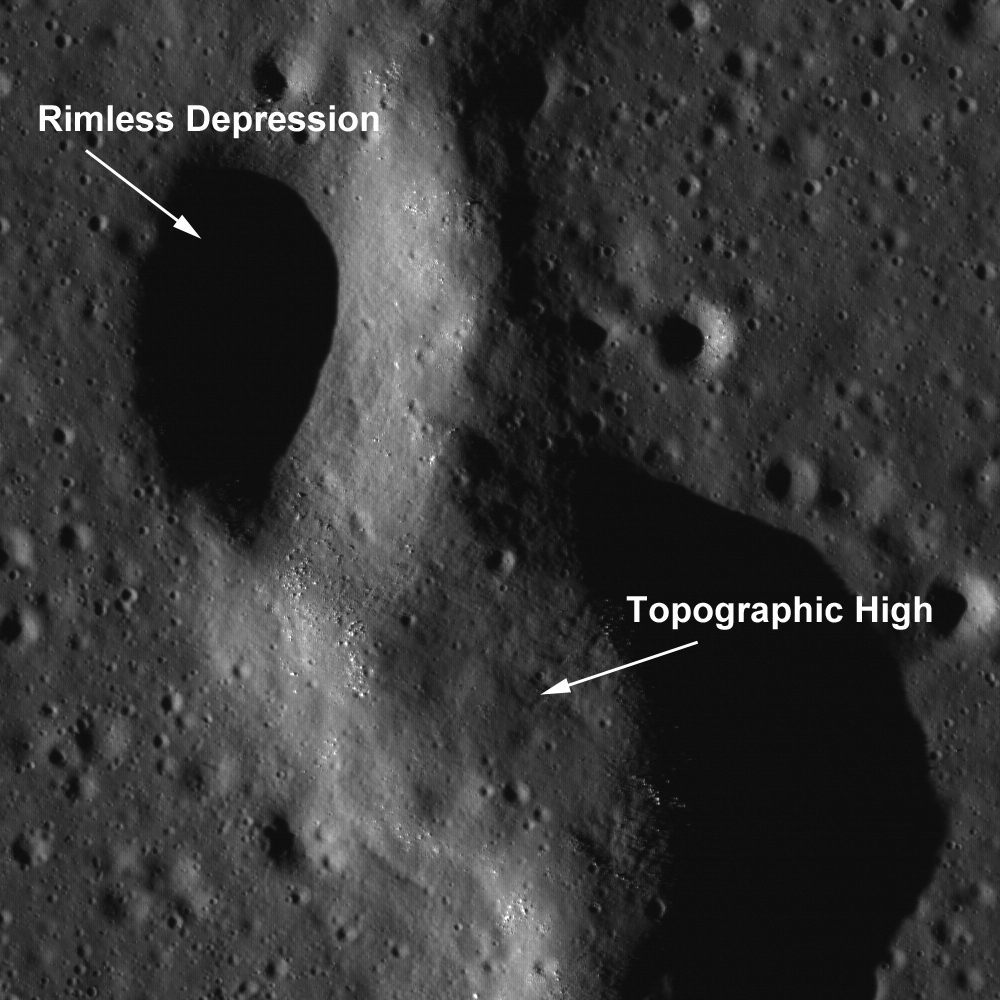
This unnamed sinuous chain of pits was suggested to be a collapsed lava tube (see Wilhelms' Geologic History of the Moon). New high resolution NAC images (e.g. M102443238R) provide a new look at the area. This particular feature transitions from a discontinuous sinuous rille into a wrinkle ridge. Some scientists have suggested that wrinkle ridge faults interact with lava tubes, with the wrinkle ridge exploiting a zone of mechanical weakness (the lava tube) in the preexisting basalt deposit. In this NAC image, the topographic depressions are non-circular, with collapse rims. Many of the pits have boulders on the interior walls. If these depressions were created by impacts, each pit would have a raised rim and an ejecta blanket.
Lava tube caves could be used during future human exploration for long-term habitation. Scientists first suggested drained lunar lava tubes as possible human habitats in 1962, and since then the possible lava tube caves have remained at the forefront of both geological debate and the future of a sustained human presence on the Moon. The lunar caves would be an ideal location for a lunar base because they a) require little construction and enable a habitat to be placed inside with a minimal amount of building, b) provide a natural environmental control (insulation and temperature stability), and c) provide protection from natural hazards (i.e., cosmic rays, meteorites, micrometeorite impacts, impact crater ejecta). On Earth, our atmosphere protects us from cancer-causing radiation, but the Moon has no atmosphere and therefore astronauts must find an alternate means of shelter, especially during times of high radiation, like solar flares and coronal mass ejections.
Geologists suspect that lunar lava tubes form similarly to terrestrial lava tubes. However, lunar lava tubes are likely much larger, due to the lower gravity and the lack of an atmosphere. Studies of lava tubes on Earth show that most are hollow. If lunar lava tubes form in a similar way, then they too are most likely hollow. A lava tube may form when an active basaltic lava flow develops a continuous crust. For instance, an open lava channel may form a crust of hardened rock that extends from the sides and, over time, meets in the middle, forming a roof. Even if a lava tube develops a roof, it still has lava running through it. There is a possibility that the cooling lava would solidify inside the tube and block it. However, on Earth most lava tubes do not "plug up." As the rate of lava flowing from the source diminishes over time, the level of liquid in the tube drops, leaving an empty space between the top of the flow and the roof of the tube.
Browse the thrilling full-resolution NAC !!!
Related Featured Images:
Natural Bridge on the Moon, Depths of Mare Ingenii, and Marius Hills Pit - Lava Tube Skylight?
Published by Sarah Braden on 17 February 2011